The turkey industry is one of the most important sectors in poultry farming, so it is necessary to know the protozoa that can impact this industry.
Turkey industry is one of the most important in poultry farming worldwide. Therefore, it is of great importance to know the infectious diseases that can affect this type of poultry production. Among the most important pathogens are the protozoa.
Protozoa are unicellular living organisms of the protist kingdom that live in humid or aquatic environments. Some of them are parasites of vertebrate animals such as turkeys, which is why they generate diseases in them.

Turkey consumption in the world: the current situation
According to 2019 figures, the turkey industry generated around USD 12.9 billion. The largest consumer of turkey meat was the United States with 2.4 million tons. This figure represents 41% of total consumption in the world. In second place is Brazil with 560,000 tons, Germany with 475,000 tons. On the other hand, Israel is the country with the highest per capita turkey consumption with 11 kg.
In terms of production, the United States is the largest turkey producer in the world with 2.7 million tons, representing about 45% of the world total. In second place is Brazil and in third place is Germany. In addition, the largest exporters of this product are the United States and Poland with 24% and 21% of the world total, respectively.
The United States is the largest consumer and producer of turkey worldwide. The state with the highest production of turkey meat in that country is Minnesota with 40 million turkeys raised, followed by North Carolina with 31 million, Arkansas with 30 million, Indiana with 16 million, and, closing the TOP 5, is Missouri with 16 million. Other states with important turkey production are Virginia, Iowa, and California.
On the other hand, the largest importers of turkey are Mexico, Canada, Japan, Peru, and Hong Kong.
Statistics estimate that about 88% of Americans consume turkey during Thanksgiving. Among the most consumed turkey products are whole turkey, ground turkey, and cooked white meat.
About 293 million Americans enjoy and prepare turkey throughout the year, especially in December, generating revenues of approximately USD 927 million. Turkey is the fourth most consumed animal protein in the United States after chicken, beef, and pork.
To meet the high demand for this poultry protein, the poultry industry has expanded and become more technified in recent decades, and currently generates 20,000 to 25,000 jobs in the United States.

Protozoan Diseases Affecting Turkey
There are four main protozoan diseases affecting turkeys: coccidiosis, trichomoniasis, cryptosporidiosis, and histomoniasis. There is another disease called Cochlosomiasis, although it is uncommon. They usually cause digestive signs in turkeys, causing diarrhea, dehydration, weight loss, and death.
Coccidiosis
Coccidiosis is a protozoan disease caused by the genus Eimeria. In this genus, several species affect poultry. In turkeys, the species mainly described are summarized in Table 1.
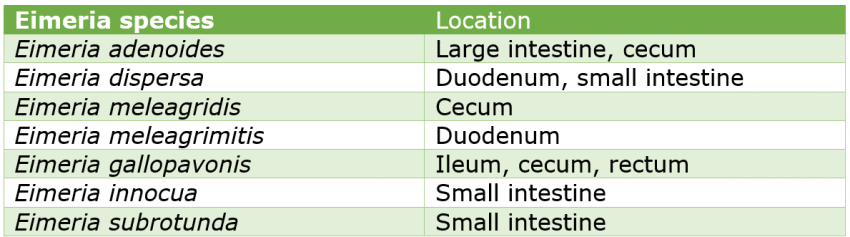
This disease generates lesions at the intestinal level that vary in their location according to the species of Eimeria involved. In addition, the disease picture can vary in severity depending on several factors associated with flock immunity, biosecurity, and management, the use of anticoccidials and, the state of the intestine, among others.
It is currently considered one of the most important diseases in turkey poultry farming due to the economic losses it generates associated with morbidity, mortality, and treatment costs.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is a protozoan disease caused by the parasite Trichomonas gallinae. This protozoan is distributed worldwide and affects turkeys, pigeons, chickens, and wild birds. In turkeys, lesions are in the esophagus, pharynx, and crop. It causes rapid loss of body weight, ruffled feathers, crowding, and lethargy. These lesions form caseous inflammations and necrosis that can affect organs.
Trichomoniasis lesions are commonly described as “yellow buttons”. Turkeys become infected by consuming water contaminated with fecal matter from pigeons or other poultry.
Cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis is a disease caused by the protozoan Cryptosporidium meleagridis. This pathogen affects turkeys, chickens, ducks, and parrots. It is distributed worldwide. Cryptosporidiosis causes diarrhea and mortality in turkeys, chickens, ducks, and parrots from 10 to 14 days of age. The protozoa are in the proventriculus and intestine, although they can also reach the lung during their cycle. Diarrhea appears due to atrophy of the intestinal villi.
This protozoan disease is transmitted mainly by the oro-fecal route and is difficult to control. Control measures focus on handling and biosecurity.
It should be noted that it is a zoonotic disease and the third most common type of Cryptosporidium infecting humans.
You may also be interested in Ochratoxin A and its impact on intestinal welfare in poultry
Histomoniasis
Histomoniasis in turkeys is also called “blackhead” or enterohepatitis. This disease is caused by the protozoan Histomonas meleagridis, which is in the cecum and liver. It is distributed worldwide and can affect turkeys, pheasants, and rarely chickens. It affects young poultry under 14 weeks of age causing necrosis in the cecum and liver.
Young turkeys with histomoniasis may die in one to two weeks if not treated. In older birds, the disease can be chronic and if they survive, the poultry becomes immune. Sometimes it can cause cyanosis of the head, which is why it is called “blackhead”, but it is not always observed.
Transmission of histomoniasis is through a nematode parasite called Heterakis gallinarum. Turkeys become infected when they consume the eggs of the nematode, inside which the protozoan is found.
Cochlosomiasis
Cochlosomiasis is a rare disease caused by the protozoan Cochlosoma anatis that affects turkeys and ducks. Not much is known about its pathogenic impact in poultry, although it is associated in co-infections with viruses, bacteria, and other protozoa. It possibly causes gastrointestinal alterations that aggravate infectious conditions. It can cause episodes of diarrhea and weight loss, affecting mainly young poultry.

Control strategies for protozoan diseases in Turkeys
Protozoan diseases affecting turkeys can be prevented by various control strategies. These measures focus on reducing the parasite load in the environment and the poultry, as well as on the supply of natural products that optimize the immunity of the poultry and restore intestinal welfare.
- Maintain optimal hygienic conditions in the facilities and sheds where the poultry are housed, ensuring that the litter has the lowest possible humidity.
- Establish health programs related to. However, in each region, these measures may vary depending on the availability of vaccines, approved biologicals, the sanitary status of the region, and resistance against anticoccidials.
- Review of water sources and water and feed supply systems to avoid contamination by fecal matter from wild birds.
- Ensure proper ventilation of the poultry house to reduce humidity and therefore the likelihood of coccidia oocysts to develop.
- Cleaning and disinfection of drinkers and feeders when changing flocks to avoid recirculation of protozoa in the environment.
- Heat treatments at 50% of the litter for 24 hours can destroy the number of oocysts during the resting period of the house.
- Administering Alquernat Coneb, a product with intestinal conditioner and optimizer pronutrients, that has proven to be efficient against protozoa in poultry. This product stimulates the regeneration of the intestinal mucosa and promotes the recovery of its integrity. In addition, it optimizes the local immunity of the intestine to improve the poultry’s response to protozoan infections such as Histomonas, Cochlosoma, Trichomonas, and coccidia.
Finally, Alquernat Coneb is a natural product that offers other advantages in the control of protozoan infections in turkeys. This product does not create resistance, does not need a withdrawal period, and has no adverse effects on the animals, making it an excellent alternative for the control of these diseases.
CONCLUSIONS
The turkey industry is a very important sector within the poultry industry. The United States is one of the largest producers of turkey in the world, generating important economic income. Thus, turkey poultry farming is considered an important production line in this sector that has been growing rapidly in recent years.
Therefore, it is of great interest to know the diseases caused by protozoa that infect turkeys and cause great economic losses.
Among the protozoan diseases of turkeys is coccidiosis caused by several species of Eimeria that injure different portions of the poultry intestine. Trichomoniasis, cryptosporidiosis, and histomoniasis are also among the most frequent. In addition, a disease called Cochlosomiasis has been described in turkeys.
Finally, several control strategies are recommended in the prevention of these diseases, focused on biosecurity and optimization of immunity and intestinal welfare of the poultry.